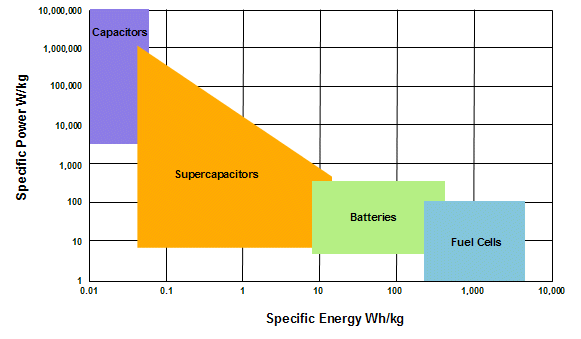
Energy storage devices may be broadly characterized by their
energy density (energy stored per unit volume or mass) and by their
power (how fast that energy can be delivered from the device).
Conventional capacitors have enormous power but store only tiny
amounts of energy. Batteries can store lots of energy but take a long time
to charge up or discharge, which means they have low power.
Supercapacitors offer a unique combination of high power and high energy properties, bridging the
gap between batteries and capacitors.
On the far end, fuel cells operate most efficiently over a narrow range
of performance parameters and at elevated temperature, rapidly becoming inefficient under high power
demands. They can be used in tandem with either batteries or supercapacitors to provide a high-energy,
high-power combination.
See "Energy Storage Technologies:
A Comparison" for more information.